#include <stdio.h> #define ROWS 3 #define COLS 3 void matrixMultiply(int *mat1, int *mat2, int *result, int rows1, int cols1, int cols2) { int i, j, k; // Multiplying matrices for (i = 0; i < rows1; i++) { for (j = 0; j < cols2; j++) { *(result + i * cols2 + j) = 0; for (k = 0; k < cols1; k++) { *(result + i * cols2 + j) += *(mat1 + i * cols1 + k) * *(mat2 + k * cols2 + j); } } } } void displayMatrix(int *mat, int rows, int cols) { int i, j; // Displaying matrix for (i = 0; i < rows; i++) { for (j = 0; j < cols; j++) { printf("%d\t", *(mat + i * cols + j)); ...
Write and explain the following types of functions with the help of an example program for each (i) Function with no arguments and no return value. (ii) Function with arguments and no return value
hello
Write and explain the following types of functions with the help of an example program for each
Write and explain the following types of functions with the help of an example program for each
(i) Function with no arguments and no return value.
(ii) Function with arguments and no return value.
ANS-
1: Function with no arguments and no return value:
In this type the function has no arguments, it doesn't receive any data from the calling function.
Similarly it doesn't return any value, the calling function doesn't receive any data from called function.
So there's no digital communication between calling function and called function.
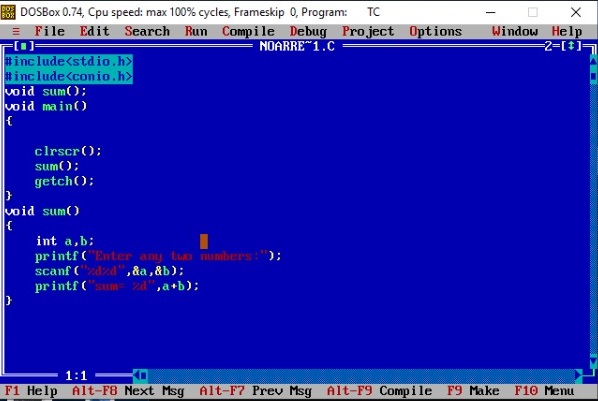
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void sum();
void main()
{
clrscr();
sum();
getch();
}
void sum()
{
int a,b;
printf(”Enter any two numbers:”);
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
printf(”sum= %d”,a+b);
}
- In this function no return and no argument means create sum function.
- no any return type, void is no return type data type.
- all processing is done inside of sum function body because no argument type means no any value return then input inside of function, declare scanf() in inside of function.
- no return any value then defined print any value inside of function.
- void main (int a, int b) is called argument then not valid in this type function because no argument .
- return (a); is return value is not valid in this concept.
- all kind of processing inside of fuction and only call in main function.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
void sum(int,int);
int a,b,s;
clrscr();
printf(”Enter any two numbers :”);
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
sum(a,b);
getch();
}
void sum(int x,int y)
{
printf(”sum= %d”,x+y);
}
- Here x, y are formal argument and a,b are actual arguments.
- In this question argument with no return type we see function declaration, the argument are formal but when value are passed (a, b ) to the function call, they are actual argument a and b.
- In this function is all processing in main function and print other function.
- we can see program defined two function, first function is main function and second function is user defined function sum.
- we can see sum function passing parameter (argument) is x and y is formal argument but we can see main function passing argument sum function a and b .actual argument.
- sum function get a argument to value and print value.
- First point value processing inside in main function.
- and call sum function in main and pass argument in sum function and get value sum function and print a value.


Comments
Post a Comment